slap tear test biceps|slap tear locations : solutions The Biceps Load II test is designed to detect SLAP lesions in the shoulder. [1] [2] Technique. Biceps Load II test technique. The patient is in the supine position with the shoulder in 120 degrees of elevation and full external rotation, while .
WEBJoining one of our popular Casino Affiliate Programs and earn money with your website. Make money with the Best Online Gambling Affiliate Program, High up to 45% Revenue Share - Mr Bet Partners.
{plog:ftitle_list}
A Ferramenta de busca e análise de criativos e funis de vendas, a solução completa integrada com algoritmos poderosos de inteligencia artificial para te entregar de .
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint problem. It’s also called the active compression test. See moreYour shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See more
Healthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See moreThe purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder .
The S in SLAP refers to the top of your labrum. When this part of your labrum tears, your upper arm bone loses its cushion and your bicep tendon loses its connection to .The Biceps Load II test is designed to detect SLAP lesions in the shoulder. [1] [2] Technique. Biceps Load II test technique. The patient is in the supine position with the shoulder in 120 degrees of elevation and full external rotation, while . A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and . SLAP tears are sometimes a result of or found in combination with biceps tendonitis or a biceps tendon tear. If a biceps tendon is torn away from where it connects to the scapula bone (shoulder blade), it can tear the glenoid .
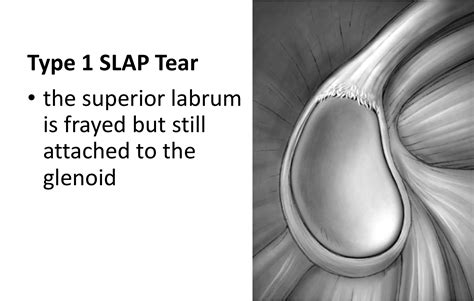
The term SLAP stands for superior labrum anterior and posterior. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. This top area is also where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. A SLAP tear extends from the front .
Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear refers to a specific injury of the superior portion of the glenoid labrum that extends from anterior to posterior in a curved .
Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are tears of the top part of the superior labrum, where the long head biceps tendon attaches. SLAP tears typically cause shoulder pain, popping and clicking and loss of shoulder function.The shoulder’s biceps muscle has two attachments: the “short head” is outside of the shoulder joint and rarely causes shoulder problems, while the “long head” travels in front of the shoulder between the rotator cuff tendons and into the . Superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions constitute a recognized clinical subset of complex shoulder pain pathologies. SLAP lesions demonstrate a predilection for young laborers, overhead athletes, and middle-aged manual laborers.[1] In 1985, Andrews first described superior labral pathologies, and Snyder later coined the term “SLAP lesion” because of the . SLAP stands for “superior labrum anterior and posterior.” The tear occurs in the top (superior) area of the labrum, where the biceps tendon is attached.
ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎ ︎ http://bit.ly/GETPT ︎ ︎OUR APPS: 📱 iPhone/iPad: https://apple.co/35vt8Vx🤖 Andro. Yergason’s test is a quick and simple physical test to help detect certain biceps tendon injuries. In particular, the test aids in the detection of an injury to the long head of the biceps tendon. It can also assist in the detecting of a tear in your transverse humeral ligament, SLAP tear and biceps tendonitis.It also assesses the ability of the transverse humeral ligament to hold the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove. The biceps tendon is associated with isolated overuse injury in youths and rotator cuff disease in the elderly. The test has been found to be more useful in diagnosing SLAP lesions than biceps diseases. Variations [edit | edit source]Biceps tendon pathology or SLAP lesion Yergasons Test; Biceps tendinopathy or Superior labral tears Speed's Test; References [edit | edit source] ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Magee, D. Shoulder. Chapter 5 In: Orthopedic Physical Assessment. Elsevier, 2014; ↑ 2.0 2.1 Biederwolf NE.
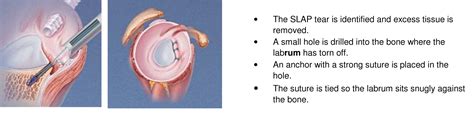
SLAP tear surgery is a procedure used to repair injured shoulder cartilage. It involves making small incisions around the shoulder joint and using specialized instruments to repair or reconstruct .Originally the Speed’s test was designed to test for tenosynovitis of the long biceps tendon but is now being used for several pathologies of the biceps. In their meta-analysis from 2012, Hegedus et al. found a sensitivity of 20% and a specificity of 78% for the Speed’s test in the detection of SLAP lesions in the shoulder.In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. This top area is also where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. A SLAP tear extends from the front (anterior) to the back (posterior) of this attachment point. The biceps tendon can be involved in the injury, as well.
A SLAP tear can be a serious injury no matter your age or professional level. The majority of SLAP tears don’t happen in one day and usually result from repetitive trauma inside the shoulder. . (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram . Tears of the labrum near the biceps tendon attachment (SLAP lesions) may be just trimmed or may .Speed's Test is used to test for superior labral tears or bicipital tendonitis. . Speed's Test ⎟ Biceps Pathology. . Accuracy of the Speed's and Yergason's test in detecting bicpes pathology and SLAP lesions: comparison with arthroscopic findings. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery, 20(3), 231-236 . Synopsis Superior labral tears (SLAP lesions) can pose a significant challenge to orthopaedic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists alike. Although advancement in arthroscopic techniques has enhanced arthroscopic repair of SLAP lesions, the clinical diagnosis of SLAP lesions can still be difficult. There is a variety of etiologic factors associated with SLAP lesions .
The Biceps Load II Test is a common orthopedic test to diagnose superior labral tears from anterior to posterior (SLAP ) lesions in the long biceps tendon of the shoulder. It was evaluated regardings its accuracy to diagnose SLAP tears by Oh et al. (2008) and Somerville et al. (2017) with a sensitivity of 30/27.6% and a specificity of 78/77.8% .SLAP tear surgery is recommended when: You still have SLAP tear symptoms despite non-surgical treatment. A specific injury caused your tear and it affects your shoulder stability. Your SLAP tear stems from overusing your shoulder. You have a SLAP tear because you regularly play sports in where you throw, such as baseball.
type 1 slap tear shoulder
slap tear surgery recovery timeline
Pathology. SLAP tears involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. Unlike Bankart lesions and ALPSA lesions, they are uncommonly (20%) associated with shoulder instability 5.. Etiology. In the acute setting, they .
The Biceps Load I proved to be one of the best tests to both rule in and rule out a SLAP tear with a sensitivity of 0.90 and a specificity of 0.96. 17 Biceps Load II also was proven to be a good indicator for ruling in or out SLAP tears having . Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .
slap tear recovery without surgery
SLAP tear symptoms generally include shoulder pain, limited range of motion, shoulder weakness and instability. . to back (posterior). This tear often affects the point where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. SLAP tears can result from acute trauma, such as falling . and areas of tenderness. They may perform specific tests, such as .
slap tear locations
The labrum also serves as an attachment site for capsuloligamentous structures, such as the glenohumeral ligaments and the long head of the biceps (Calcei et al. 2018). SLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete .A SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior) tear happens when the upper labrum is torn at or near its attachment with the biceps. A SLAP tear usually happens after heavy lifting, a repeated overhead activity (such as playing tennis or throwing a ball), a shoulder dislocation, or a fall on to your outstretched hand. SLAP tears can also be a .Biceps Load I Test to Assess SLAP Lesions. SLAP stands for a superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and mainly occurs in the overhead throwing athlete. . In 2017, Somerville et al. assessed the diagnostic accuracy of physical examination tests to diagnose SLAP tears. Among others, the Biceps Load 1 test was included based on surgeon .There are several types of labral tears: A SLAP lesion (superior labrum, anterior [front] to posterior [back]) is a tear of the labrum that usually occurs on the upper part of the socket and may also involve the origin, or starting point, of the long head of the biceps tendon.; A tear of the front part of the labrum at the bottom of the socket is called a Bankart lesion.
Purpose: The purpose of this report is to describe the biceps load test II for evaluating the superior labral anterior and posterior (SLAP) lesions.Type of Study: This is a double-blind study in consecutive data, which includes diagnostic accuracy of a test using sensitivity, specificity, and interexaminer reliability.Methods: In the supine position, the arm is .
slap tear biceps anchor
- Kim biceps load test two for SLAP lesion - Pain provocation test for SLAP lesion - Anterior glide test for SLAP tear; Figures . attachment can lead to labral injury during shoulder motions in the abducted and externally rotated positions when the biceps tendon is stretched. SLAP tears occur from several mechanisms. One mechanism involves . In the setting of failed primary SLAP repair, biceps tenodesis remains a viable option in order to eliminate the pull of the LHBT on the superior labrum. McCormick et al. presented a case series of 42 patients with an average age of 39 years old, who failed primary repair of a type II SLAP tear that underwent subpectoral biceps tenodesis [70 .

18 de mai. de 2021 · Patreon is empowering a new generation of creators. Support and engage with artists and creators as they live out their passions!
slap tear test biceps|slap tear locations